Ankle injuries are a common concern, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in physical activities. Among the various types of ankle injuries, tears or strains in the Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) are frequently encountered. These injuries can significantly impact mobility and require proper understanding, treatment, and precautions for effective healing. In this blog, we delve into the healing timeline of ATFL injuries and the essential precautions to facilitate recovery.
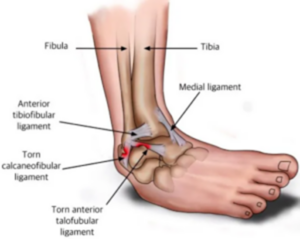
ATFL Tear: Causes and Symptoms
The Anterior Talofibular Ligament, situated on the outer side of the ankle, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the joint. An ATFL tear often occurs due to sudden twisting or rolling of the ankle, commonly experienced during sports activities like basketball, soccer, or tennis. The tear leads to symptoms such as:
Pain: Immediate pain at the time of injury, which may persist during movement.
Swelling: Visible swelling around the ankle joint due to inflammation.
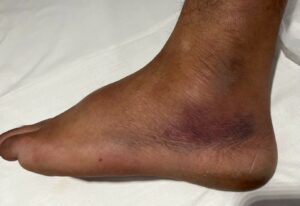
Instability: Ankle instability, making it challenging to bear weight or walk normally.
Bruising: Discoloration or bruising on the affected area, indicating tissue damage.
ATFL Treatment and Healing Time
Upon diagnosing an ATFL tear through physical examination and possibly imaging tests like MRI, the treatment approach is determined. The healing time for ATFL injuries varies depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment strategy. Generally, the healing timeline can be categorized as follows:
Mild Tears (Grade 1): These involve minor stretching or microscopic tears in the ligament. Healing typically takes around 4 to 6 weeks with conservative measures like rest, ice therapy, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol). Physical therapy may also be prescribed to improve strength and stability.
Moderate Tears (Grade 2): Injuries with partial tears or more significant damage may require 6 to 12 weeks for recovery. Immobilization with a brace or boot, along with physical therapy, is often recommended. Non-weight-bearing activities are encouraged during this phase to prevent further strain on the ligament.
Severe Tears (Grade 3): Complete tears of the ATFL or associated ligaments necessitate more intensive treatment and a longer healing period. Surgery may be considered in severe cases, especially if there are concurrent injuries or chronic instability. Post-surgical rehabilitation and gradual return to activity are crucial for optimal recovery.
Precautions for ATFL Injury Recovery
While healing from an ATFL injury, certain precautions play a vital role in facilitating a smooth recovery process and minimizing the risk of complications or re-injury:
Immobilization: Follow the prescribed period of immobilization, whether using a brace, splint, or cast, to allow the ligament to heal without excessive stress.
Weight Management: Avoid putting excessive weight or pressure on the injured ankle during the initial healing phase. Crutches or a supportive walking aid may be necessary.
Physical Therapy: Engage in a structured physical therapy program focusing on ankle strengthening, range of motion exercises, and proprioception training to regain stability and function.
Gradual Return to Activity: Progressively reintroduce weight-bearing activities and sports-specific drills under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Rushing back into strenuous activities can jeopardize recovery and lead to recurrent injuries.
Proper Footwear: Wear supportive and well-fitted footwear that provides adequate ankle support and cushioning, especially during sports or physical activities.
Avoiding Risky Movements: Be cautious of activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or uneven surfaces that could strain the healing ligament.
Regular Follow-ups: Attend scheduled follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor progress, address any concerns, and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the healing time for an ATFL injury depends on various factors such as the severity of the tear, treatment approach, and adherence to precautions. While mild tears may heal within weeks with conservative measures, more severe injuries may require months of rehabilitation and possibly surgical intervention. Adhering to precautions, following medical advice, and being patient during the recovery process are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes and preventing future ankle problems.

